The Earth’s climate has changed throughout its existence, shaped by myriad natural processes. In the contemporary context, the terms climate change and climate variability describe the Earth’s climate system alterations. While climate variability and climate change are interconnected, they are separated by their distinct characteristics.
What Is the Difference Between Climate Change and Climate Variability?
The key differences between climate change and climate variability are based on their timescales and causes.
Natural Climate Variability
Natural climate variability refers to the fluctuations in climate conditions – such as rainfall or temperature – over relatively short time scales. This can typically refer to a month, season or year. Various natural processes within the Earth’s systems can influence this, such as within the atmosphere, ocean and land surfaces.
For example, many natural processes can cause the global average temperatures to fluctuate around the average — without causing the long-term average to change. This may make a region’s temperature slightly warmer or cooler in a given month or year than the one before. Another well-understood source of climate variability is the tilt of the Earth, which causes seasonal changes in the northern and southern hemispheres.
Climate Change
Conversely, climate change refers to the long-term alterations in the Earth’s climate that may occur over hundreds or thousands of years. This has happened throughout history. However, human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation are adding more heat-trapping greenhouse gases to the air. This is warming the atmosphere, oceans and land faster than in the last 10,000 years.
Climate scientist Dr. Natalie Burls explains that human activities have dramatically increased carbon dioxide in our atmosphere over recent decades to levels not seen in millennia. “These were periods of sustained warmth that lasted over millions of years,” Dr. Burls said.
Today’s rapidly changing climate impacts the long-term balance of ecosystems supporting life, health and biodiversity. It is causing more extreme weather events, such as more intense and frequent storms, floods, heatwaves and droughts. It is also melting glaciers and ice sheets and heating the ocean, causing rising sea levels. Some of these impacts could be irreversible.
What Is an Example of Climate Change and Climate Variability?
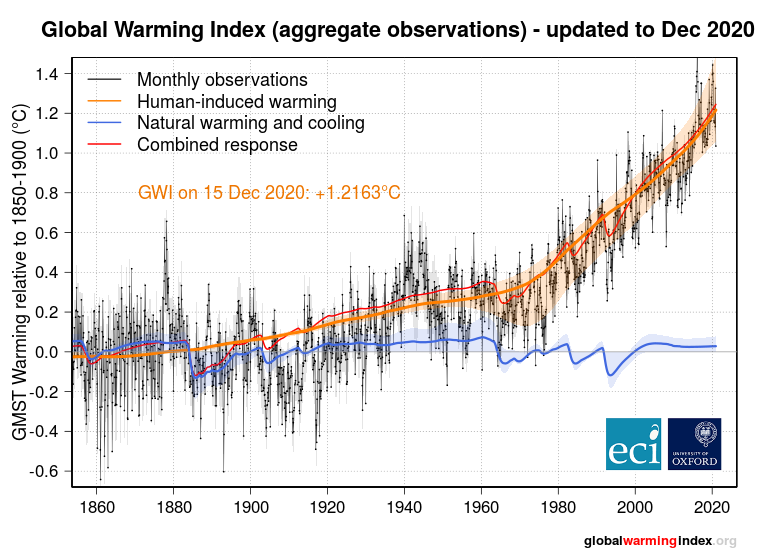
The graph below demonstrates the difference between climate change and climate variability regarding the Earth’s temperatures.
The blue line shows the Earth’s natural temperature variability since industrial times. While there are short-term fluctuations, the overall temperature trend is relatively stable.
Conversely, the orange line shows the Earth’s temperature trend is influenced by human activities, namely increasing pollution of greenhouse gas emissions. This shows a long-term upward trend, particularly since the 1960s.
Causes and Effects of Natural Climate Variability
The Earth’s complex systems include natural phenomena that cause short-term climate variability. The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle and the Asian monsoon are two key examples.
El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
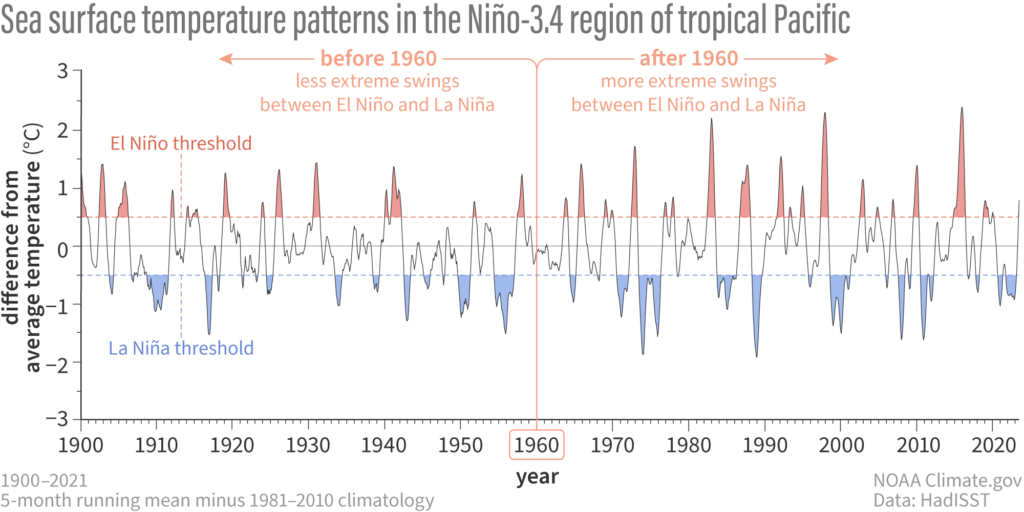
The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a natural climate pattern characterised by the periodic warming (El Niño) and cooling (La Niña) of sea surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean.
El Niño tends to bring warmer and drier conditions to some regions, such as drought in Australia and Indonesia. Conversely, La Niña often leads to cooler and wetter conditions in certain areas.
While the ENSO cycle is a central example of natural variability, research shows that human activity influences this phenomenon. Since the 1960s, climate swings between El Niño and La Niña have become more extreme. With a warmer climate meaning more severe regional rainfall events, future El Niño events will likely be much more intense, according to NASA.
The Asian Monsoon
Monsoons are natural seasonal wind patterns that bring distinct wet and dry periods to certain regions. The Asian monsoon is characterised by a shift in wind direction that brings heavy rainfall during the summer. The variability in monsoon patterns leads to natural fluctuations in rainfall, which influence agriculture, water resources and ecosystems.
However, much like the ENSO cycle, evidence is emerging that global warming is influencing this natural phenomenon. Scientists say that climate change is making monsoons more erratic, resulting in long dry periods and short spells of severe rains that make flooding and landslides destructive in monsoon regions.
Living on an Ever-changing Planet
With human activities rapidly affecting the Earth’s natural processes, ongoing research into the causes and traits of changing climatic patterns is crucial. Distinguishing between human-caused and natural factors – and their complex interactions and impacts – is vital to understanding the scale of the climate crisis caused by human activities. Addressing and adapting to these changes is crucial to allow life to flourish on this ever-changing planet.
Evelyn Smail
Writer, United Kingdom
Evelyn is a freelance writer and journalist specialising in climate science and policy, the just energy transition and the human impacts of climate change. She writes for independent publications, NGOs and environmental organisations. Evelyn has a background in sustainable development, climate justice and human rights.
Evelyn is a freelance writer and journalist specialising in climate science and policy, the just energy transition and the human impacts of climate change. She writes for independent publications, NGOs and environmental organisations. Evelyn has a background in sustainable development, climate justice and human rights.














